Operating Systems: Three Easy Pieces Ch. 39
File and Directories
- Persistence Storage
- HDD
- SSD
- Files and Directories
- inode number
- directory
- Directory tree (hierarchy)
- Root directory
- Subdirectory
- Separator
- Type of the file
- Creating file
- open()
- file descriptor
- Capability
- Reading and Writing files
- Strace
- trace the system calls made by a program
- Flags
- Strace
- Not sequential reading and writing
- random offset
- searching specific word
- File Offset
- Open file table
- OS can use this to determine whether the opened file is readable or writable (or both), which underlying file it refers to (as pointed to by the struct inode pointer ip), and the current offset (off).
- random offset
- Shared File Table Entities
- Fork and dup
- reference count
- The dup() call allows a process to create a new file descriptor that refers to the same underlying open file as an existing descriptor
- Fsync()
- (DBMS), development of a correct recovery protocol requires the ability to force writes to disk from time to time
- Renaming files
- rename() call is atomic
- Information about files
- metadata
- stat() or fstat() system calls
- inode
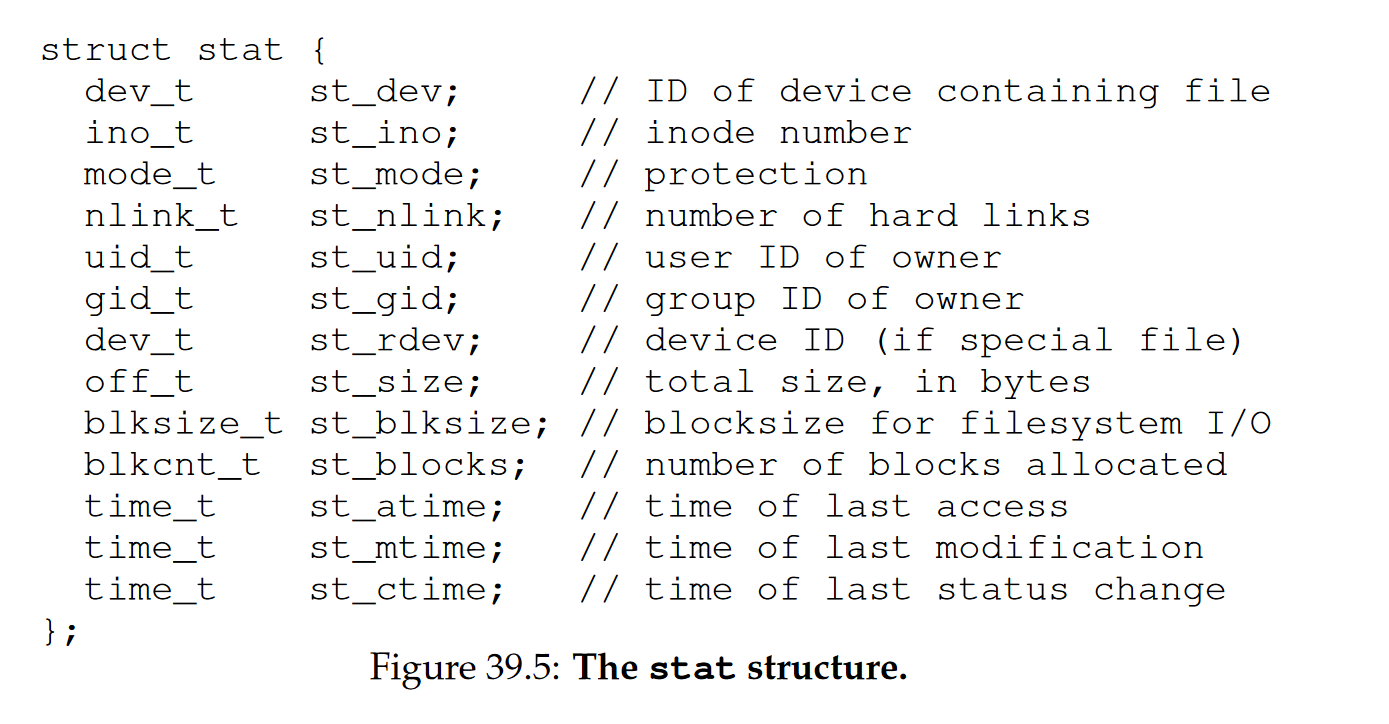
- metadata
- Removing Files
- unlink() ?
- Making Directories
- To create a directory, a single system call, mkdir(), is available. The eponymous mkdir program can be used to create such a directory.
- Reading Directories
- the program uses three calls, opendir(), readdir(), and closedir()
- struct dirent
- Deleting Directories
- rmdir()
- Hard Links
- he link() system call takes two arguments, an old pathname and a new one; when you “link” a new file name to an old one, you essentially create another way to refer to the same file
- The way link() works is that it simply creates another name in the directory you are creating the link to
- reference count (link count)
- Symbolic Links
- Soft Link
- the original file can now be accessed through the file name file as well as the symbolic link name file2.
- dangling reference possibility
- Permission Bits And Access Control Lists
- permission bits
- what the owner of the file can do to it, what someone in a group can do to the file, and finally, what anyone (sometimes referred to as other) can do.
- chmod command
- form of an access control list (ACL) per directory
- Making And Mounting A File System
- What mount does, quite simply is take an existing directory as a target mount point and essentially paste a new file system onto the directory tree at that point
- mkfs