2023-HGU-ML Lecture 10. Classification
- classification and regression
- both supervised learning
- classification
- predicting a discrete label of the input
- interested in the boundary
- regression
- predicting the quantity of output
- usually evaluated by root mean square error
- interested in the relationship between input and output
- data for supervised learning
- a row: instance
- a column: one feature or attribute
- Xn → n samples
- Y: N outputs
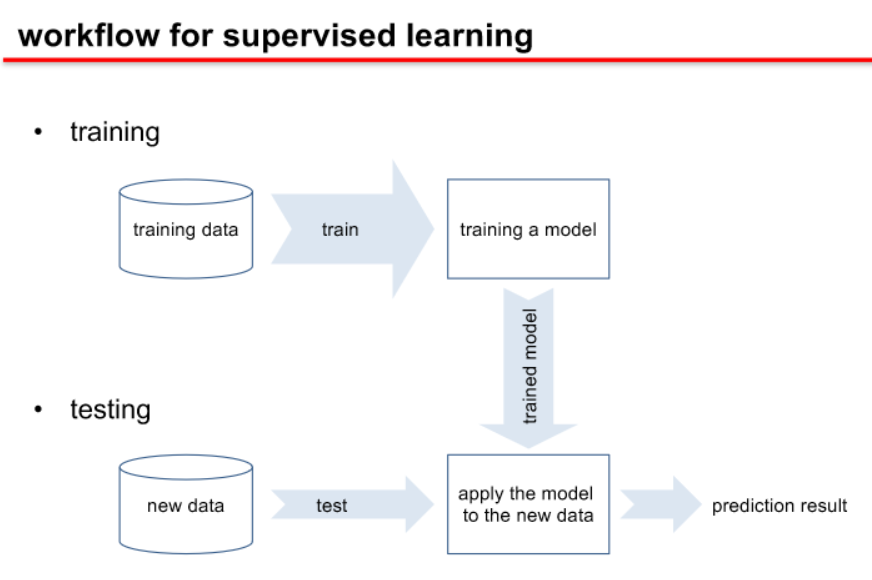
- training, validation, and testing
- training the model with training data (Xtr, Ytr)
- learning the parameters by optimizing an objective function
- validation with validation data (X val, Y val)
- to evaluate the model or to avoid overfitting
- if no validation data is available, split the data into training and validation
- test
- predicting the output of new data
- test data and training data should be separated at all.
- training the model with training data (Xtr, Ytr)
- cross-validation
- a resampling procedure to evaluate ML models on limited data
- split the data into training (including validation) and testing
- evaluate the model
- repeat the above steps
- model complexity and overfitting
- overfitting: a model is too closely fit to a limited set of training data
- to avoid
- spreading out the probability mass from the training samples
- discovering underlying abstractions/explanatory factors
- approaches
- more data
- simpler model
- regularization
- early stopping
- k nearest neighbors
- a simple form of making predictions
- instance-based approach
- to make a decision, retrieve k closest training examples in the feature space
- lazy learning
- all deferred until the prediction time

- Algorithm
- need to decide
- distance metric
- k
- how to make a prediction
- compute the distances to the training data instances
- identify k neighbors
- determine the class label of the testing instance
- need to decide
- characteristics
- simple to implement
- leads to a very simple approximation of the optimal Bayes classifier
- lazy
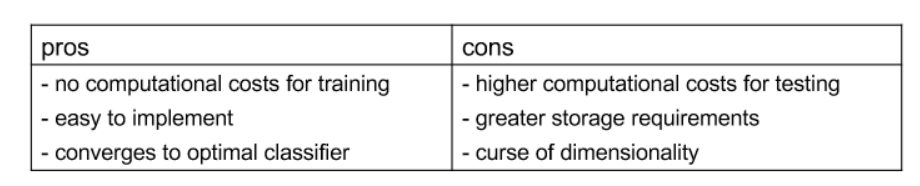
- The “curse of dimensionality” refers to various challenges and phenomena that arise when working with high-dimensional data. As the number of features or dimensions in a dataset increases, certain issues and complexities emerge that can affect the performance of algorithms and the interpretation of results
- To solve the issue
- bucketing
- k-d tree
- metric learning
- feature-weighting
- distance-weighting
- Under or overfitting
- K is too small
- sensitive to noisy data
- overfitting to training data
- K is too large
- no-sensitive to data
- underfitting
- smoother decision regions, destroying the locality of the estimation
- burden
- K is too small
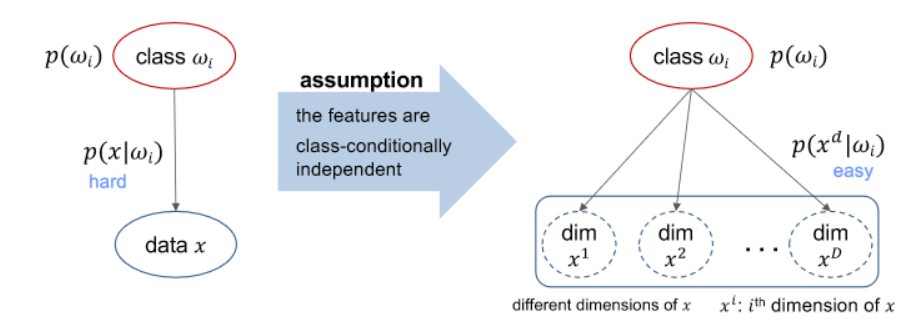
- naïve Bayes classifier
- for classification, what we want is posterior

- assuming that the features are class conditionally independent
- The Naïve Bayes classifier is a probabilistic machine learning algorithm based on Bayes’ theorem.
- It assumes that features are conditionally independent given the class label, simplifying the computation of the posterior probability. Despite its simplistic assumption, Naïve Bayes is widely used for classification tasks and is particularly effective in text categorization, spam filtering, and other applications where independence assumptions hold reasonably well.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Naive_Bayes_classifier
- decision tree (DT)
- a tree-shaped prediction mode
- decision-based on a tree
- a non-metric method
- without a measure of distance between features
- can work with nominal data
- Prediction and Training
- prediction: given a decision tree, how can we make predictions for new data?
- when the instance arrives at a leaf node, take the node’s decision
- training: given a dataset, how can we select a feature and make a branch?
- the most common training strategy for a given dataset
- start from an empty decision tree
- on each node, split the set in the node into subsets based on a metric
- until the subset at a node has all the same value
- top-down induction of decision trees (greedy algorithm)
- Metrics
- classification
- Minimize Gini Impurity
- Gini impurity: measures how often a decision would be incorrect if it was randomly labeled according to the distribution of labels in the subset
- maximize information gain
- Information Gain: calculates the decrease in entropy after the dataset is split on a feature
- Minimize Gini Impurity
- regression
- minimize variance and std
- a weighted average of MSE from two nodes
- classification
- interpretability of decision tree
- in business, interpretability is also important as well as accuracy
- importance value in the decision tree
- measures decrease in node impurity weighted by the probability of the node
- or measures decrease in MSE for regression

- to overcome overfitting
- early stopping
- readjusting
- random forest
- the most common training strategy for a given dataset
- prediction: given a decision tree, how can we make predictions for new data?
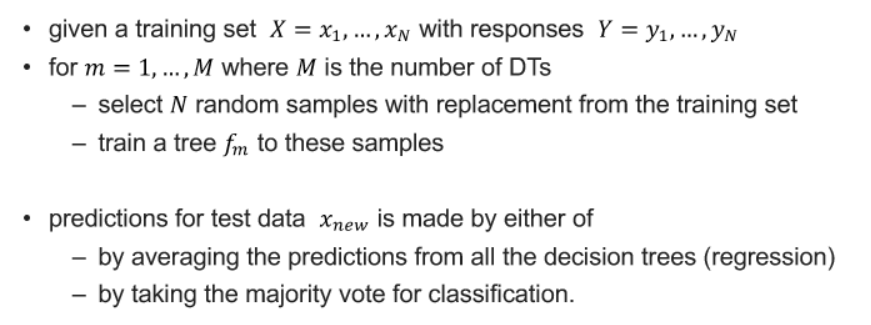
- Random Forest
- ensemble learning method by constructing a set of decision trees
- algorithm
- applies the committee method to the decision tree

- For feature importance
- permutation
- train the baseline model and record the score
- for all, randomize the values
- calculate new scores
- difference of the score → feature importance
- dropping a column
- compare a score with all features and a score with one feature dropped
- accurate, but expensive
- compare a score with all features and a score with one feature dropped
- permutation